Mesonutrients and meso-dosing are the latest buzz words in nutritional circles and curious health enthusiasts are becoming more and more interested to learn about them. These terms are new to most people, and mesonutrients are touted as the latest health trend of 2019.
So what are mesonutrients and meso-dosing and how can you boost your health with them? How do you incorporate these nutrients into your diet? In this article, we’ll find out more about mesonutrients and hopefully address any questions you may have regarding this newest health trend.
What Are Mesonutrients?
You no doubt know that macronutrients refer to proteins, carbohydrates, and fats. They are responsible for fueling our body with energy. On the other hand, micronutrients refer to vitamins and minerals that help in the healthy development of our body. Both macronutrients and micronutrients are important in promoting overall health and wellness.
Aside from the macronutrients and micronutrients, there are other hidden nutrients from certain foods that can also provide nourishment for our body and these are the mesonutrients.
Derived from the term “meso”, which means middle, mesonutrients basically refer to those “in-between” nutrients that we tend to miss out on our everyday diet. These active compounds are being hailed as the super powers hidden inside so called superfoods that help to provide our body with rich antioxidants leading to numerous health benefits.
I have to say here that “superfood” is not a scientific term. It’s a word dreamed up by marketing people. The correct term used in science is
“Functional food”. They are foods that contain nutrients which can have health-promoting properties, such as reducing the risk of disease or improving physical or emotional health.
Meso-dosing refers to the way of getting more of the active compounds in superfoods to maximise their health benefits. Health companies are now producing mesonutrients in powder and supplement form. For example, as well as drinking green tea for the antioxidant polyphenols in it, you could take a green tea extract.
Boosting Health With Mesonutrients
Mesonutrients are present in foods like blackberries, tomatoes, turmeric, green tea and other superfoods. According to research, mesonutrients may help to lower the risk of certain cancers, improve brain functioning, reduce inflammation, enhance energy, and could possibly help with weight loss.
Although mesonutrients are not entirely new, recent studies show that we may be able to reap more health boosting benefits from these superfoods if we include them in our diet and consume them in higher doses.
Antioxidants are important to have in our diets to quench free radicals. Our body is constantly creating these unstable molecules through breathing, digesting food, detoxification and exercising. Antioxidants produced in the body from vitamins and minerals we get from food can keep these under control.
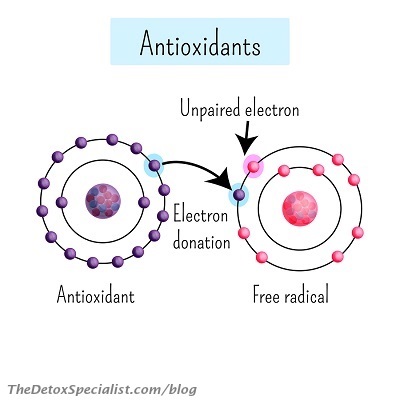
External toxins like air pollutants, cigarette smoke, UV rays from the sun, toxins in food like pesticides, heavy metals, and other toxins and contaminants create a massive amount of free radicals that can easily overwhelm our body’s capacity to deal with them. Free radicals, if left unchecked, damage cells eventually leading to a range of diseases and aging. That’s where these other antioxidants like the mesonutrients come in.
Foods Rich in Mesonutrients
You can incorporate mesonutrients into your diet by simply eating certain superfoods. Below are some of the mesonutrients that are present in certain foods.
Anthocyanins
Anthocyanins are mesonutrients that are naturally found in purple and red foods. These mesonutrients act as antioxidants that have powerful anti-viral and anti-inflammatory benefits. There is a lot of interest in them for their brain and heart protecting properties. There are also studies that show anthocyanins may promote weight loss and prevent the development of breast cancer cells.
So, if you want to benefit from these, simply make sure you include grapes, acai berries, kidney beans, pomegranates, cranberries, cherries and lesser known bilberries and chokeberries in your diet.
Meso-doses used in clinical trials ranged from 80 mg – 450 mg of anthocyanidins a day. 250g blueberries would give you about 250g so it’s not difficult to obtain from your diet.
Curcumin
Curcumin is the mesonutrient found in turmeric, which is one of the most popular superfoods in the world. Turmeric is used to improve a wide range of conditions, including arthritis, rheumatoid arthritis and ulcerative colitis thanks to its powerful anti-inflammatory effects.
But the health benefits of turmeric actually came from the active ingredient, curcumin, which is also known to be a prebiotic. However, the concentration of curcumin in raw turmeric is low and it’s difficult for our gastrointestinal tract to absorb curcumin on its own. The best way to incorporate curcumin into your diet is to consume it in the form of supplements.
Piperine, an active compound in black pepper, is known to improve the bioavailability of curcumin in the body and many supplement manufacturers are add piperine to curcumin supplements.
Another way to improve the absorption of curcumin is to use turmeric root (fresh or dried as a powder) because natural oils found in turmeric root and turmeric powder can enhance the bioavailability of curcumin seven to eight fold. According to Dr Greger curcumin can be directly absorbed into the bloodstream when eaten with fat, through the lymphatic system.
Epigallocatechin Gallate
Epigallocatechin Gallate, also known as EGCG, is found in green tea and also in white tea in lesser amounts. This antioxidant mesonutrient has been found to prevent cell damage so has cancer-fighting benefits. It could potentially prevent cancer cells from further developing and impede the formation of blood vessels in tumors.
It has also been touted as an anti-aging ingredient and has been shown to improve insulin sensitivity which may help prevent Type 2 diabetes. Some studies have shown that EGCG has anti-infective properties as well as antiviral activities.
One of the best ways to include EGCG in your diet is through matcha tea which is particularly high in catechins, the antioxidant found in green tea. You can make it into a latte or drink it as a smoothie.
For meso-dosing, intakes of 270 mg – 600 mg a day have been shown to have health boosting benefits. Much higher higher amounts have been associated with reversible liver damage in rare cases. Joshua Lambert, an assistant research professor in the Department of Chemical Biology at Rutgers University states:
To date, there have been nine anecdotal case reports of liver toxicity in humans associated with consumption of high doses [700–2,000 mg/day] of green tea from dietary supplements.
It’s hard to say how much ECGC is in tea because the chemical composition of green tea varies widely due to plant variety, growing environment, season, age of leaves and manufacturing conditions. There is concern over taking high doses of green tea extract supplements for weight loss.
Researchers say the liver toxicity could be due to contaminants in the tea. A few years ago Consumer Labs found that a number of popular brands of green tea contained lead but they said that the lead stayed in the leaves and did not get into brewed tea.
Having said that most studies have found that green tea drinkers are in better health than those who do not drink tea at all. They drink a lot of the stuff in China and Japan so it can’t be bad. It’s a case of every good thing in moderation. More is not always better. We have to be careful to have a balance.
Lycopene
Lycopene is a mesonutrient that you’ll find in red-colored foods, such as tomatoes. Although all mesonutrients are known for being high in antioxidants, lycopene is said to have the highest amount of antioxidants, powerful enough to neutralize the harmful free radicals in the body.
It’s high antioxidant properties means it’s also good for your skin. Some studies indicate that it can help to reduce skin reactions if you get too much sun.There is also evidence that it can lower LDL (bad) cholesterol and increase levels of HDL (good) cholesterol.
Aside from tomatoes, you can also find it in watermelon, pink grapefruit, papaya, canned and fresh tomatoes, tomato puree and cooked sweet red peppers. By simply eating lots of these foods, you’ll be able to help protect your body against environmental damage.
Intakes of 8mg -21 mg are said to be the most beneficial and there is approximately 3 mg in 100g of tomatoes.
Resveratrol
Resveratrol is derived from dark-colored berries and some plants. It’s been shown to have lots of health benefits such as the potential to support cardiovascular health and provide anti-aging benefits.
It may affect enzymes known as sirtuins, which are involved in the aging process. You can find out more about sirtuins in my article about The Sirt Diet. Some of the most common sources of resveratrol are red wine, red grape juice, cranberries, blueberries, cocoa, dark chocolate, pistachios, and mulberries.
There are is no officially recommended dosage for resveratrol, but supplements of this polyphenol are usually taken in doses of 50-250 mg per capsule and up to 250 – 500 mg per day. You should probably not take resveratrol supplements if you are taking anti-coagulant medication (blood thinner).
Safranal
Derived from saffron, grown in Middle East and parts of Europe and said to be the most expensive spice in the world. American saffron or Mexican saffron is derived from safflower and is not the same as true saffron which comes from the stigmas of Crocus sativus.
Saffron from dried flowers from safflower give the characteristic yellow color to foods, but not the distinctive pungent flavor of true saffron. The best quality saffron is reputed to be cultivated in Iran, Kashmir and Spain.
Safranal is a type of mesonutrient that is thought to promote mental health. It is thought that it help to balance neurotransmitters such as dopamine and serotonin although there is no conclusive research on it. One study though concluded that it was as good a the antidepressant drug Prozac for treating mild to moderate depression.
Saffron has been used traditional medicine for centuries to prevent hair loss, boost digestive health, and alleviate symptoms of premenstrual syndrome. It may also help to suppress appetite and boost libido.
30 mg of saffron per day has been shown to be enough to get its health benefits although up to 1.5 grams a day can be taken in supplement form. One of the best ways to incorporate this mesonutrient into your diet is to use it in rice or vegetable dishes or drink saffron tea. The pungent flavor can be disguised by adding other spices like ginger and cinnamon and sweetened with a little raw honey or a natural sweetener like monk fruit or a good quality stevia. No sugar please!
Conclusion
There are definitely lots of benefits that you can get by adding mesonutrients into your daily diet. But this does not mean that macronutrients and micronutrients are no longer important. You still need your proteins, carbohydrates, fats, vitamins, and minerals, which you may not be able to obtain just by eating the foods listed above. Therefore, the key to good health is to balance your macros, micros, and mesonutrients.
If you want to eat more of the superfoods mentioned above in order to benefit from its mesonutrients, make sure you make it a part of a healthy and well-balanced diet. Above all it’s probably best to consult a well informed nutritionist or Naturopath before taking any form of supplements.




